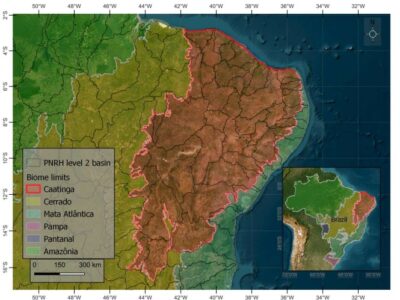
Rocha et al – Mapping Burned Area in the Caatinga Biome: Employing Deep Learning Techniques
O bioma semiárido Caatinga é particularmente suscetível à dinâmica do fogo. As secas periódicas amplificam os riscos de incêndio, enquanto as actividades antropogênicas, como a agricultura, a expansão de pastagens e o desmatamento, contribuem significativamente para a prevalência dos incêndios. Esta pesquisa tem como objetivo avaliar a eficácia de um modelo de detecção de incêndios e analisar os padrões espaciais e temporais de áreas queimadas, fornecendo insights essenciais para estratégias de manejo e prevenção de incêndios. Utilizando modelos de redes neurais profundas (DNN), mapeamos áreas queimadas em todo o bioma Caatinga de 1985 a 2023, com base em mosaicos de qualidade anuais derivados do Landsat e valores mínimos de NBR. No período de 38 anos, o modelo classificou 10,9 Mha (12,7% da Caatinga) como queimados, com área queimada média anual de aproximadamente 0,5 Mha (0,56%). O pico de área queimada atingiu 0,89 Mha em 2021. As cicatrizes do incêndio variaram significativamente, variando de 0,18 Mha em 1985 a flutuações substanciais nos anos subsequentes. O tipo de vegetação mais afetado foi a savana, com 9,8 Mha queimados, enquanto as florestas sofreram apenas 0,28 Mha de queimadas. Outubro surgiu como o mês com maior actividade de incêndios, contabilizando 7266 hectares. Estas descobertas sublinham a complexa interacção de factores climáticos e antropogénicos, destacando a necessidade urgente de estratégias eficazes de gestão do fogo.
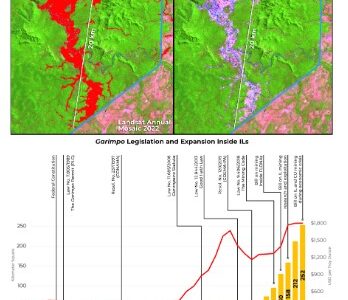
Ferreira Neto et al – Uncontrolled Illegal Mining and Garimpo inthe Brazilian Amazon
Mining has played an important role in the economies of South Americancountries. Although industrial mining prevails in most countries, the expan-sion of garimpo activity has increased substantially. Recently, Brazil exhibitedtwo moments of garimpo dominance over industrial mining: 1989–1997 and2019–2022. While industrial mining sites occupied ~ 360 km2 in 1985 butincreased to 1800 km2 in 2022, a 5-fold increase, garimpo mining areaincreased by ~ 1200%, from ~ 218 km2 in 1985 to ~ 2627 km2 in 2022. More than91% of this activity is concentrated in the Amazon. Where almost 40% of thesites are five years old or younger, this proportion increases to 62% withinIndigenous lands (ILs). Regarding the legal aspect, at least 77% of the 2022extraction sites showed explicit signs of illegality. Particular attention must begiven to the Kayapo, Munduruku, and Yanomami ILs. Together, they con-centrate over 90% of the garimpo across ILs.

Souza et al – Amazon severe drought in 2023 triggered surface water loss
O trabalho tem como objetivo apresentar uma estimativa da extensão da perda de água na Amazônia brasileira em 2023, devido à seca severa provocada pelo El Niño e pelo aquecimento dos oceanos. A pesquisa estima a perda de 3,3 milhões de hectares de água superficial, destacando as áreas mais afetadas, especialmente nos estados do Amazonas e Pará, e os impactos significativos em rios e na biodiversidade aquática. Além disso, avalia como essa perda afeta comunidades tradicionais, como indígenas e extrativistas, e ressalta a vulnerabilidade dessas populações às mudanças climáticas. Por fim, o artigo defende a criação de um sistema de monitoramento integrado para melhorar a compreensão dos impactos climáticos e facilitar a resposta adequada a essas questões.

Rocha et al – Towards Uncovering Three Decades of LULC in the Brazilian Drylands: Caatinga Biome Dynamics (1985–2019)
This article aims to analyze changes in land use and land cover in the Caatinga biome in Brazil over a span of 35 years, from 1985 to 2019. Through a collaboration with the MapBiomas project and utilizing Landsat data, the study provides a detailed view of the transformations in the Caatinga landscape. The results highlight a significant reduction in natural vegetation, mainly due to the expansion of cattle ranching and agriculture, and underscore the importance of understanding these changes for the development of social, economic, and environmental policies for the region and other dryland areas around the world.

Arruda et al – Assessing four decades of fire behavior dynamics in the Cerrado biome (1985 to 2022)
This article analyzes four decades of fire data in the Brazilian Cerrado (1985–2022) using annual fire maps. The study reveals that 40% of the biome has been affected by fires, with an increase in both the frequency and size of burned areas, primarily due to human ignitions and agricultural expansion. The article also highlights the need for conservation strategies, such as Integrated Fire Management, to mitigate these impacts and enhance climate resilience.

Souza et al – Landsat sub-pixel land cover dynamics in the Brazilian Amazon
This study proposes a novel approach to characterize and measure land cover dynamics in the Amazon biome. First, we defined 10 fundamental land cover classes: forest, flooded forest, shrubland, natural grassland, pastureland, cropland, outcrop, bare and impervious, wetland, and water. Second, we mapped the land cover based on the compositional abundance of Landsat sub-pixel information that makes up these land cover classes: green vegetation (GV), non-photosynthetic vegetation, soil, and shade. Third, we processed all Landsat scenes with <50% cloud cover. Then, we applied a step-wise random forest machine learning algorithm and empirical decision rules to classify intra-annual and annual land cover classes between 1985 and 2022. Finally, we estimated the yearly land cover changes in forested and non-forested ecosystems and characterized the major change drivers.

Baeza et al – Two decades of land cover mapping in the Río de la Plata grassland region: The MapBiomas Pampa initiative
This work describes and analyzes the land cover changes in the entire Río de la Plata Grasslands (RPG) region for the first two decades of the 21st century, especially those related to grassland loss. In 20 years, RPG region lost, at least, 2.4 million ha of grassland (9% of the remaining grassland area in 2001). Most of these losses are concentrated in Brazil and Uruguay and are associated with new agricultural or forestry areas that increased by 5% and 100%, respectively.

Alencar et al – Long-Term Landsat-Based Monthly Burned Area Dataset for the Brazilian Biomes Using Deep Learning
The paper presents a new strategy using machine learning to map monthly burned areas from 1985 to 2020 using Landsat image mosaics and minimum NBR values. This new dataset contributes to the understanding of the long-term spatial and temporal dynamics of fire regimes that are fundamental to designing appropriate public policies to reduce and control fires in Brazil.

Cayo et al – Mapping Three Decades of Changes in the Tropical Andean Glaciers Using Landsat Data Processed in the Earth Engine.
This paper presents the mapping and retreat dynamics of tropical Andean glaciers (TAGs) from the use of Landsat time series images from 1985 to 2020, with digital processing and classification of the satellite images on the Google Earth Engine platform.

Coelho-Junior et al – Unmasking the impunity of illegal deforestation in the Brazilian Amazon: a call for enforcement and accountability
This article provides a perspective on the dynamics of deforestation alerts, validated and refined by MapBiomas Alert (http://alerta.mapbiomas.org/), in the Brazilian Amazon and the actions of federal and state public enforcement agencies highlighting the urgency to reduce and combat deforestation.